Did you know?
Globally, around 1.4 million cases of hepatitis A are reported annually and there are approximately 300 million carriers of
hepatits B virus worldwide.1,2 In Singapore, about 4% (1 in 25 persons) of the population has chronic hepatitis B infection.3
Viral hepatitis are infectious diseases which cause the inflammation of the liver. Some of the most common types of viral hepatitis include hepatitis A and hepatitis B, which are caused by the hepatitis A virus (HAV) and hepatitis B virus (HBV) respectively.4
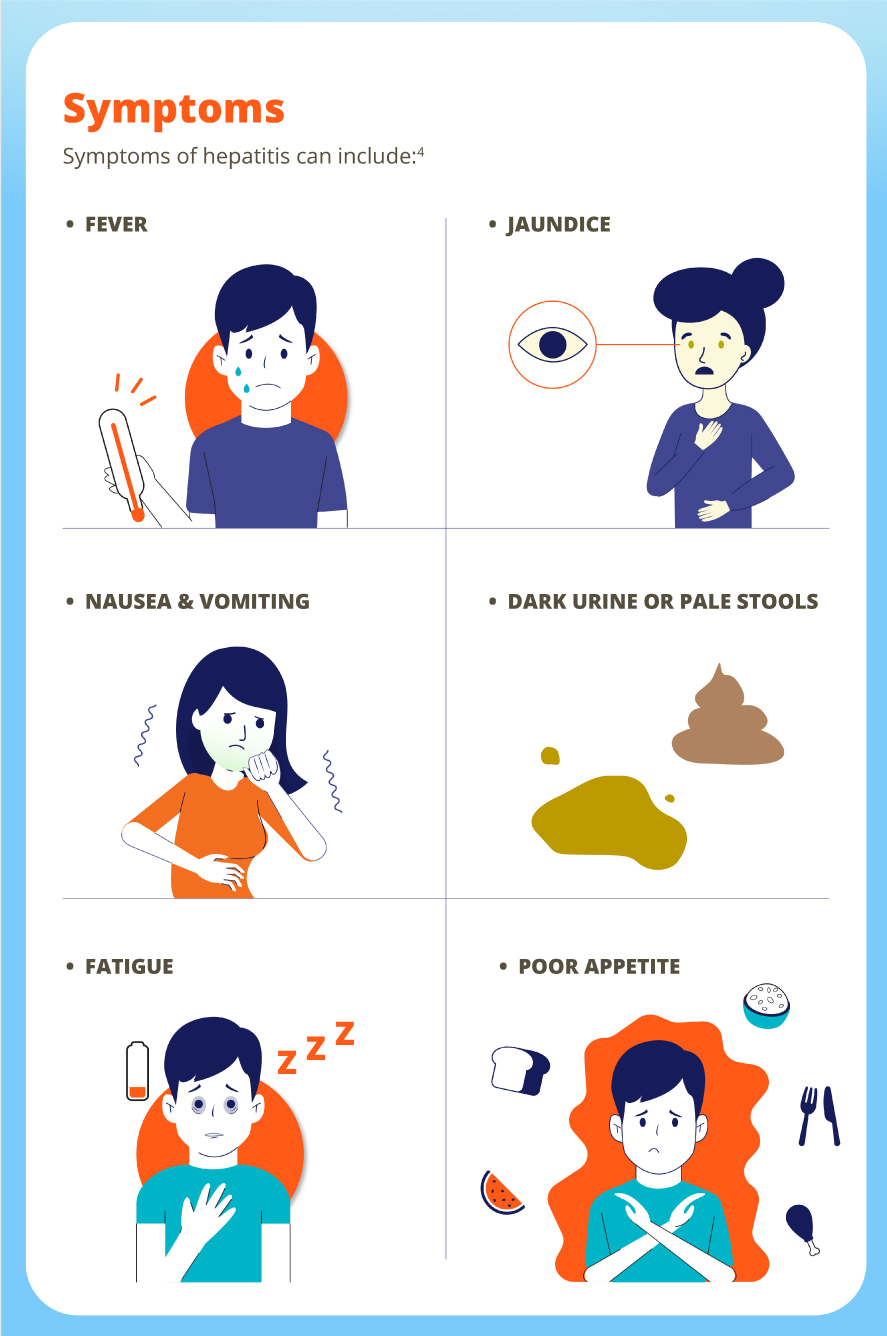
Many people with hepatitis do not have symptoms but can still spread the infection.5,6 If symptoms occur with an acute infection, they can appear anytime from 2 weeks to 6 months after exposure.4
Impact on health
Hepatitis A:
- Relapsing signs & symptoms for up to 6 months.11
- Although very rare, death can occur.4
- Most recover with no lasting liver damage although recovery from symptoms following infection may be slow and can take
several weeks or months.4,9
- There is no specific treatment for hepatitis A.9
Hepatitis B:
- 15%–25% of chronically infected people develop chronic liver disease, including liver inflammation, liver failure, or liver cancer.4,12
- May lead to liver cirrhosis (scarring and damage of liver) which may require a liver transplant.12
How can i protect myself?
Who is at risk of hepatitis?
| Hepatitis A |
Hepatitis B |
- Travellers to intermediate and high-risk areas*.13
- Young children living in areas where the disease is prevalent.13
- Patients with chronic liver disease.14
- People who may be exposed to hepatitis A through their jobs
(e.g., sewage workers).14
*High-risk areas: South Asia (India, Pakistan, Bangladesh).15
*Intermediate-risk areas: Central Asia (Uzbekistan, Kazakhstan,
Azerbaijan), Oceania (Fiji, Solomon Islands, Papua New Guinea),
Middle East (Egypt, Iran, Turkey), Latin America (Andean, Central,
Southern, Tropical Regions).15 |
- Infants born to infected mothers.10,12
- People who may have occupational exposure (e.g., healthcare workers, public safety workers).10,12
- Travellers who have not completed their hepatitis B vaccination.10
- Patients on haemodialysis.10
- Everyone born before 1987, when the National Immunization Program for hepatitis B was introduced in Singapore.16
|
Get protected against hepatitis
According to Centers of Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the best way to protect against Hepatitis A and B is through vaccination.5,17
Singaporeans can use Medisave to fund their hepatitis B vaccination. Patients with complex chronic conditions will be able to use up to $700 per patient yearly, while other patients will be able to use up to $500 per patient yearly.20
Please consult your healthcare professionals for more information on the disease.
Footnote:
All Singapore Citizens (SCs) and Permanent Residents (PRs) who meet the criteria for vaccination under the National Childhood Immunisation Schedule (NCIS) and National Adult Immunisation Schedule (NAIS) are eligible for subsidies for nationally-recommeded vaccinations.21
References
- WHO. Immunization, Vaccines and Biologicals. Hepatitis A. Available at: https://www.who.int/immunization/diseases/hepatitisA/en/. Last accessed September 2022.
- WHO. Hepatitis B Key Facts. Available at: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hepatitis-b. Last accessed September 2022.
- NUH. Hepatitis B. Available at: https://www.nuh.com.sg/Health-Information/Diseases-Conditions/Pages/Hepatitis-B.aspx Last accessed September 2022
- CDC. What is Viral Hepatitis? Available at: https://www.cdc.gov/hepatitis/abc/index.htm Last accessed September 2022.
- CDC. Hepatitis A Questions and Answers for the Public. Available at: https://www.cdc.gov/hepatitis/hav/afaq.htm#C2 Last accessed September 2022.
- CDC. Hepatitis B Questions and Answers for the Public. Available at: https://www.cdc.gov/hepatitis/hbv/bfaq.htm Last accessed September 2022.
- CDC. Hepatitis A. Available at: https://www.cdc.gov/hepatitis/hav/index.htm Last accessed September 2022.
- WHO. Chapter 3 Microbiological hazards. Available at: https://www.who.int/water_sanitation_health/bathing/recreaII-ch3.pdf?ua=1; Last accessed September 2022.
- WHO. Hepatitis A Key Facts. Available at: https://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hepatitis-a# Last accessed September 2022.
- CDC. Hepatitis B Questions and Answers for Health Professionals. Available at: https://www.cdc.gov/hepatitis/hbv/hbvfaq.htm#overview Last accessed September 2022.
- CDC. Epidemiology and Prevention of Vaccine-Preventable Diseases - The Pink Book: Course Textbook-2015. Available at: https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/-pubs/pinkbook/downloads/hepa.pdf Last accessed September 2022.
- Healthhub. Hepatitis B. Available at: https://www.healthhub.sg/a-z/diseases-and-conditions/48/HepatitisB Last accessed September 2022.
- WHO. Weekly epidemiological record N0. 28-29, 2012. Available at: https://www.who.int/wer/2012/wer8728_29.pdf?ua=1 Last accessed September 2022.
- NHS. Overview Hepatitis A. Available at: https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/hepatitis-a/Last accessed September 2022.
- Jacobsen KH, Wiersma ST. Hepatitis A virus seroprevalence by age and world region, 1990 and 2005. Vaccine, 2010;28:6653-7. Last accessed September 2022.
- MOH. Communicable Diseases Surveillance in Singapore 2005. Available at: https://www.moh.gov.sg/docs/librariesprovider5/resources-statistics/reports/childhood_immunisation1fe282548a9e4e06a0a00c497a8acb27.pdf Last accessed September 2022.
- CDC. Global Immunization: Preventing Hepatitis B. Available at: https://www.cdc.gov/globalhealth/immunization/othervpds/preventing_hepatitisb.html Last accessed September 2022.
- SIDS. Handbook on Adult Vaccination in Singapore 2020. Available at: https://cfps.org.sg/assets/CPG/SIDS-Adult-Vaccine-Handbook-2020.pdf Last accessed September 2022.
- MOH. Nationally recommended vaccines. Available at: https://www.moh.gov.sg/resources-statistics/nationally-recommendedvaccines Last accessed September 2022.
- MOH. MediSave. Available at: https://www.moh.gov.sg/cost-financing/healthcare-schemes-subsidies/medisave Last accessed September 2022.
- MOH. Vaccination and childhood developmental screening subsidies. Available at: https://www.moh.gov.sg/cost-financing/healthcare-schemes-subsidies/vaccination-and-childhood-developmental-screening-subsidies Last accessed September 2022.