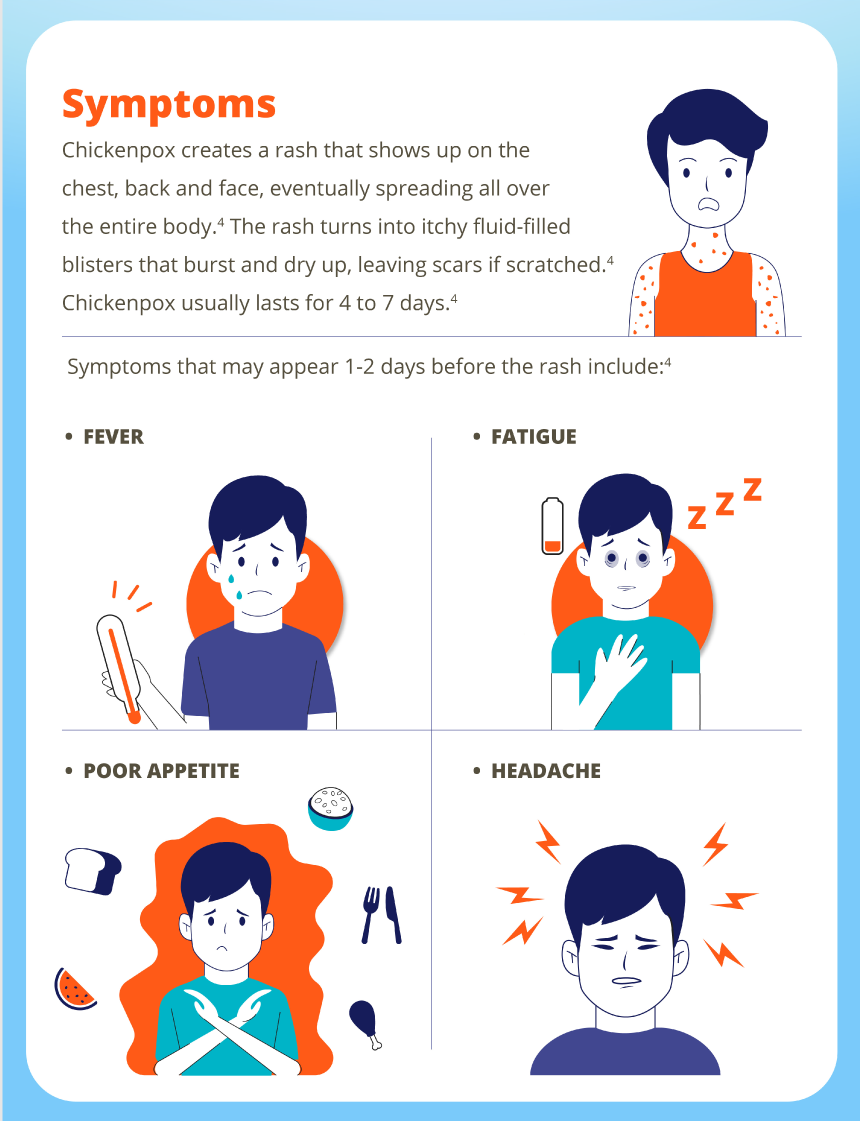
Did you know?
In Singapore, the incidence is around 500 cases per 100,000 population.1 Chickenpox is a highly contagious disease caused by the varicella-zoster virus.2 It can cause up to 500 itchy and blister-like rashes that spreads over the entire body.2
While chickenpox is more common in children, its effects are often more severe in adults.3
Impact on health
Complications of a chickenpox infection include:11
- Dehydration
- Brain damage from encephalitis (inflammation of the brain)
- Pneumonia
- Arthritis (joint pain, stiffness and swelling)
Chickenpox can also cause serious health risks for pregnant women and their baby.5 Complications related to chickenpox in pregnancy vary
depending on the gestation period in which chickenpox is contracted:
- First 20 weeks of pregnancy – the baby faces a slight risk of birth defects known as congenital varicella syndrome.5
- Few days before delivery to 48 hours postpartum – the baby might be born with neonatal varicella, a potentially life-threatening infection.5
- Pregnant mothers can get pneumonia if chickenpox is contracted during pregnancy.5
Get protected
Who is at risk?6
- Newborns and infants of unvaccinated mothers or mothers who have yet to contract chickenpox.
- Pregnant women who have yet to contract chickenpox.
- Immunocompromised individuals due to medications or medical conditions like the Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) infection.
- People taking steroid medications.
Vaccination
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends Varicella Vaccine vaccination as the best way to prevent chickenpox.2
- Singapore’s National Childhood Immunisation Schedule (NCIS) recommends for all children to receive the Varicella Vaccine (VAR).7
- Children, adolescents and adults should get vaccinated even if they have never had chickenpox or were never vaccinated.7
- People considering pregnancy who have yet to contract chickenpox or were never vaccinated should also receive the VAR.5 However, pregnant women should not receive the vaccine, and pregnancy should be avoided for 3 months after receiving the vaccine.8
All Singapore Citizens (SCs) and Permanent Residents (PRs) who meet the criteria for vaccination under the National Childhood Immunisation Schedule (NCIS) are eligible for subsidies for nationally-recommeded vaccinations.9
Singaporeans can use Medisave to fund their Varicella vaccination. Patients with complex chronic conditions will be able to use up to $700 per patient yearly, while other patients will be able to use up to $500 per patient yearly.10[RT2]
Please consult your healthcare professionals for more information on the disease.
References
- Chickenpox In: Ong A, Goh KT, eds. A Guide on Infectious Diseases of Public Health Importance In Singapore (7th Edition). Singapore: Ministry of Health; 2011.
- CDC. About Chickenpox. Available at: https://www.cdc.gov/chickenpox/about/index.html. Last accessed September 2022.
- Healthhub. Chickenpox: Symptoms and Treatment Options. Available at: https://www.healthhub.sg/a-z/diseases-and-conditions/94/topics_chickenpox. Last accessed September 2022.
- CDC. Chickenpox. Signs and Symptoms. Available at: https://www.cdc.gov/chickenpox/about/symptoms.html. Last accessed September 2022.
- Mayo Clinic. Healthy Lifestyle: Pregnancy week by week. Available at: https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/pregnancy-week-by-week/expert-answers/chickenpox-and-pregnancy/faq-20057886. Last accessed September 2022.
- Mayo Clinic. Chickenpox. Available at: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/chickenpox/symptoms-causes/syc-20351282. Last accessed September 2022.
- MOH. Nationally Recommended Vaccines. Available at: https://www.moh.gov.sg/resources-statistics/nationally-recommended-vaccines . Last accessed September 2022.
- NHGP. Vaccination Clinic: Chickenpox Vaccine. Available at https://www.nhgp.com.sg/Our_Services/Other_Services/Vaccination_Clinic/. Last accessed September 2022.
- MOH. Vaccination and Childhood Developmental Screening Subsidies. Available at: https://www.moh.gov.sg/cost-financing/healthcare-schemes-subsidies/vaccination-and-childhood-developmental-screening-subsidies. Last accessed September 2022.
- MOH. Medisave. Available at: https://www.moh.gov.sg/cost-financing/healthcare-schemes-subsidies/medisave. Last accessed September 2022.
- CDC Chickenpox complications https://www.cdc.gov/chickenpox/about/complications.html